Evaluating the potential for success and expectations of soon-to-be-launched new products or the capacity to learn and assimilate information are critical components of both market research and education.
As a result, employing evaluation metrics from the beginning of product conception to its completion, surveys are always necessary and should not be disregarded or carried out randomly.
Table of Contents
Among many survey instruments, rating scales are very beneficial, efficient, and widely used. Thus, the article will discuss rating scale examples and how to use them in designing a research questionnaire.
What is A Rating Scale?
The rating scale is one of the most commonly used questions for online surveys. Based on the closed-ended question format, presents respondents with a question and then a series of options for them to select their answer from.
Rating Scale Examples in Research and Survey
Rating scales are commonly used in many different fields. It is a common method of data collection that is used to gather comparative information about a specific research subject. In particular, a rating scale is a kind of multiple-choice question that enables survey participants to rate a good or service. For instance, firms use rating scale questions in their survey most of the time. For example, they are frequently found in customer feedback questionnaires, to assess overall satisfaction with a good, service, or encounter. How satisfied are you with your most recent purchase, on a scale of 1 to 10? Did you purchase a newspaper recently?
Below, I’ve placed the list of the most common rating scale examples with explanations used in research and education.
Numerical Rating Scale
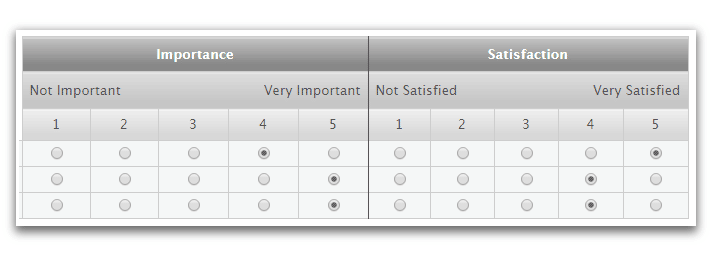
One kind of rating scale that asks respondents to provide their answers as numerical values is called a numeric scale. To enable respondents to quantify their opinions, this kind of rating scale equates comparative survey response options to an ordered set of numerical values. On a standard scale of 0 to 10, where 0 denotes no symptoms or experience and 10 denotes the worst symptoms or experience that can exist, respondents are asked to rate their experiences.
The researcher can view survey responses in quantitative notation with this kind of rating scale. To quantify qualitative data like pain, feelings, product satisfaction, chance of recommendation, customer loyalty, and the like, numerical rating scales are frequently used.
Tips: Surveys almost universally adhere to the standard that the lowest number, either 0 or 1, represents a pain point and the highest number, the highest positive rating. Adhere to this norm instead of the opposite, as this could mislead customers and prompt them to share false information.
Examples
- “On a scale of 1 to 10, how satisfied are you with our product/service?”
- “Please rate the ease of use of our product on a scale from 1 to 5.”
- “Please rate your overall satisfaction with the training program on a scale from poor (1) to excellent (5).”
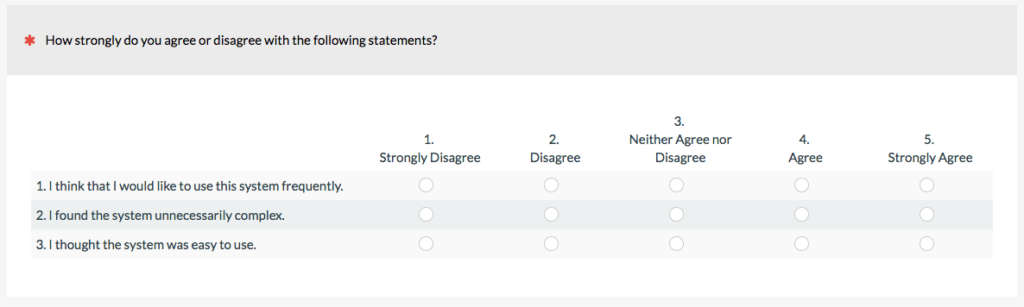
Likert scales are widely used as a dependable method of measuring attitudes, perceptions, and behavior. They bear the name of their creator, American social scientist Rensis Likert.
Likert scale ratings are designed to offer quantitative response options that facilitate data analysis. Additionally, respondents’ responses regarding their opinions of the good or service were more detailed.
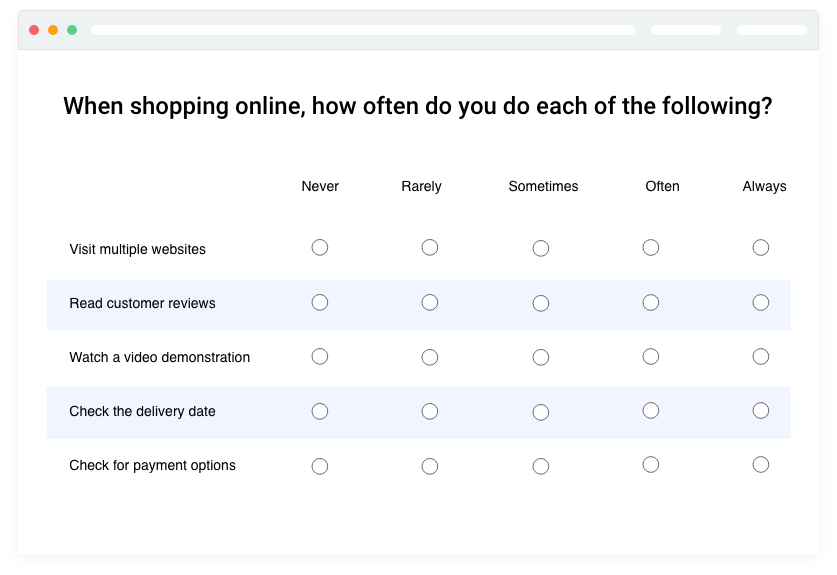
For customer service research, Likert scale responses are flexible and can be used to gauge a range of emotions, including consent, satisfaction, frequency, and desirability. For instance, frequency responses (e.g., Never, Rarely, Sometimes, Frequently, Frequently)) will be useful if you are curious about how frequently customers use your online help portal.
Tips: Set of questions in your survey center around the same subject. In the end, this will enable you to obtain more precise outcomes.
Examples
“How satisfied are you with the variety of products available in our store?”
- Very Dissatisfied
- Dissatisfied
- Neutral
- Satisfied
- Very Satisfied
“How likely are you to recommend our service to a friend?”
- Very likely
- Likely
- Unsure
- Unlikely
- Very unlikely
Slider
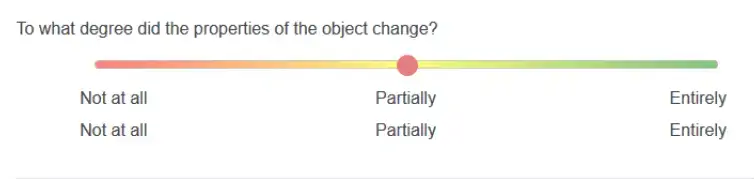
The kind of graphical rating question is the sliding bar question. To answer a question or rate their feeling, respondents are not required to enter any text or number. Slider rating scales facilitate animation and interactivity and let researchers create question-and-answer formats with a wider range of possible answers.
A slider scale is a viable alternative to the limitations of a multiple-choice question or a Likert scale question type because it allows for a broader range of responses. There are two main types of sliding scale questions: numerical slider and text slider:
- Numerical Slider
- Text Slider
Tips: Ensure that each question is pertinent to the slider scale you are using. Remember to include the proper question category tags, labels, and descriptions in your survey so that respondents know exactly what they’re answering!
Examples:
- How satisfied are you with our product? (0: Very dissatisfied, 100: Very satisfied)
- How often do you exercise? (0: Never, 100: Always)
- How likely are you to buy from us again? (0: Very unlikely, 100: Very likely)
- Star Rating
One popular type of rating survey is the use of star ratings as response options for customers to answer questions on a rating scale. Customers are asked to select how many stars they would like to give a specific product, service, or company in a star rating survey.
With a star rating scale, respondents can indicate how satisfied or dissatisfied they are with a product or service by assigning a number to the item. Researcher marketer uses stars on a scale to represent ranked attributes rather than checkboxes, numbers, or radio buttons.
Tips: Steer clear of leading questions. Leading questions slant the answer recipient’s response in one direction or the other.
Examples
- How would you rate the quality of our product? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
- How satisfied are you with our service? ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
More Tips When Designing Rating Scale Questionnaire in Research and Education
To take full advantage of the rating scale, in addition to understanding it and its application types, you can follow some of the instructions below.
- Choose the query you want to ask
- Make a scale
- Test both your scale and your question
- Gather and evaluate the data
- Share your information
How to Create an Online Survey with a Rating Scale Online?
It is easy to design a rating scale questionnaire in your survey. The best way to do it is using a free online survey creator. The editor introduces AhaSlides, one of the free survey creators that offers easy-to-use rating scales that allow you to create pleasant and easy paths to useful feedback. Make a unique and professional rating scale with AhaSlides in three easy steps.
Step 1: Formulate your query
Are you curious about whether customers love your product or detest the delivery time? Ask the big question, complete the statements, and wait for the revelations to come to you.
Step 2: Set the scale label in step two.
The wording and quantity of the values on your scale are addressed in the “scale” section.
You can increase the five values that come with the standard AhaSlides scale slide to any number you’d like (below 1000).
Step 3: Distribute your survey to the respondents
To begin a live poll, select the ‘Present’ button. In the Settings, select the ‘Self-paced’ option if you wish to survey the audiences over a specific time frame. Once the survey link is shared, you can proceed.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of rating scales?
A rating scale is an assessment tool or system for evaluating and rating the performance, behavior, abilities, or other relevant characteristics of individuals, products, services, or any other topic of interest.
Why do we need a rating scale?
The rating scale is useful in both education and the workplace. Rating scales can be used to evaluate students’ abilities, attitudes, or performance in process areas such as communication skills, linguistic skills, level of participation, and interest in the topic.
Besides, a researcher may ask respondents to rate a product feature on a scale of one to ten. One can represent a very dissatisfied respondent, while ten represents a very satisfied respondent. This is a rating scale example.
Ref: Indeed
Level up your presentations! Discover online tools with aneasytool.com that ignite your creativity and elevate your presentation skills.




